Powering Your Vehicle
Necessary to start any gas-fueled combustion engine, spark plugs send high voltage electricity to one end and ignite a spark at the other end. The spark fires the air and fuel mixture within the engine and creates the combustion that powers your car. Read on to learn more about the components that make up a spark plug.

What is the design of a spark plug?
The design of the spark plug hasn’t changed much since the inception of the combustion engine in the late 1800s. A central electrode that carries the current runs the entire length of the spark plug. The spark plug wires (if applicable – older technology) or the ignition coil connects to the top of the spark plug’s electrode. A ceramic insulator separates the electrode from the rest of the spark plug.
The plug is screwed into the cylinder head and protrudes into the combustion chamber with a threaded metal section, called the ground point of the spark plug. At the bottom of the spark plug is a small metal piece that looks like a “J” sitting sideways – this is the side (or ground) electrode. There is a gap between the center electrode and the side (ground) electrode, which is where the spark jumps the gap.
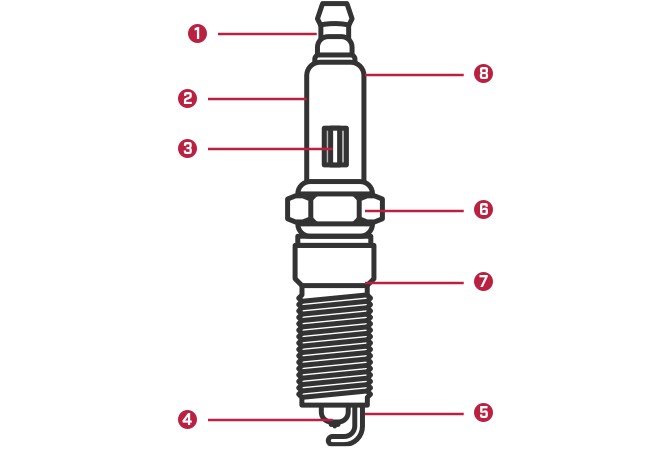
Connects to the ignition system and conducts the high voltage to the central electrode.
Insulates the terminal, center shaft and center electrode against high voltage and provides flashover protection. Keeps high voltage from escaping before it gets to the electrode tip.
Suppresses ignition noise that is generated during sparking. Helps prevent electrical interference with other electrical components in the vehicle and disruption to radio reception.
Connects to the terminal by an internal wire. Tip is made of copper, nickel, chromium or other precious metals. The metal carries the high voltage through the spark plug so it can spark when it goes across the small gap between the central electrode and the side electrode.
Located on the side of the metal, it extends into the combustion chamber to create the spark that ignites the fuel.
Steel shell where a socket wrench fits for tightening and loosening the plug. Provides electrical ground to cylinder head and transfers heat to the head to help cool the plug.
Located between the insulator and the housing, it helps keep combustion gases from escaping.
Helps stop voltage from jumping to the hex head.
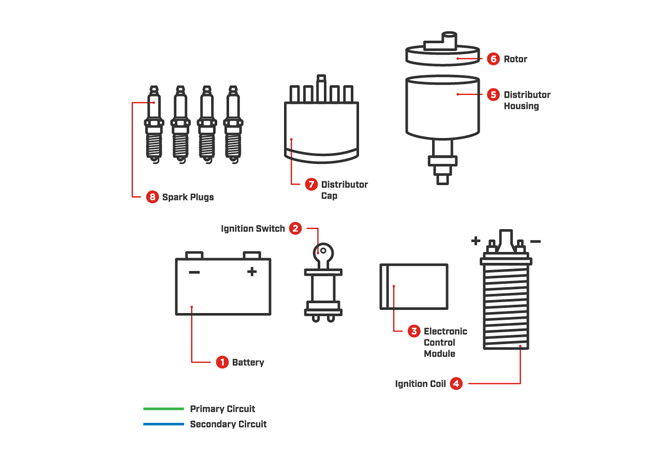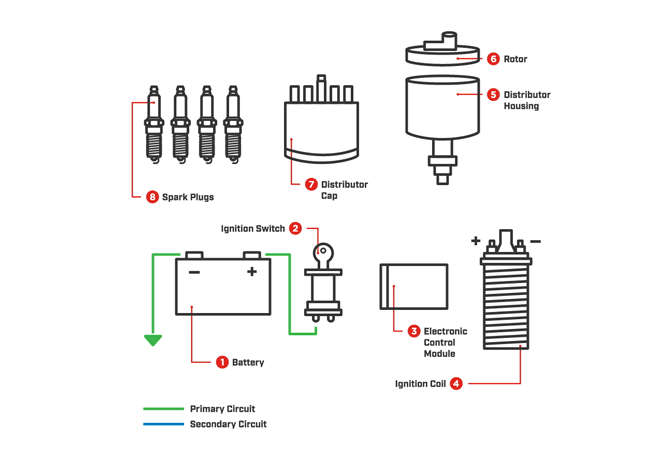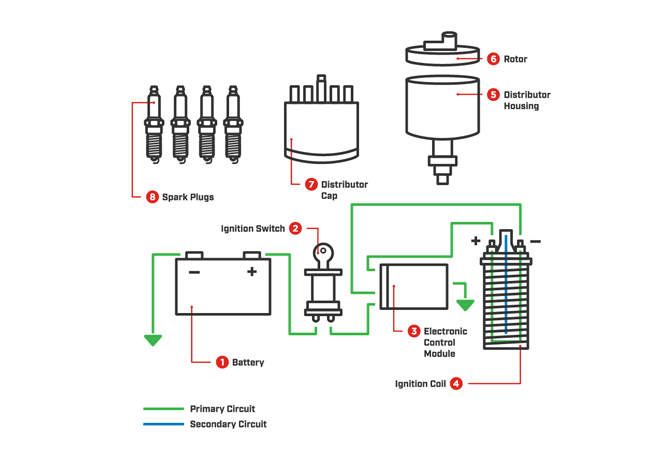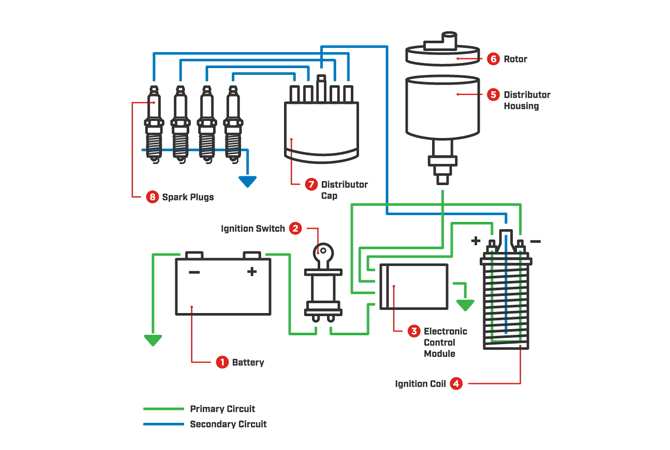
How do spark plugs work in my engine?
The spark plugs are typically located at the top of the cylinder head. The piston moves down the cylinder where it take in a combination of air and fuel. Next, the piston travels back up to the spark plug, compressing the mixture.
When the piston is at top dead center, the ignition coil sends voltage out to the spark plug generating a spark and firing off the air/fuel mixture. The piston then travels back down, generating power for the vehicle. The piston then travels back to the top and pushes the exhaust out on its way up. At this point, the whole process starts over again. Thanks to this combustion event, your vehicle has the power it needs to run.
Learn more about quality spark plugs, find your part, or find where to buy your part today.
The content contained in this article is for informational purposes only and should not be used in lieu of seeking professional advice from a certified technician or mechanic. We encourage you to consult with a certified technician or mechanic if you have specific questions or concerns relating to any of the topics covered herein. Under no circumstances will we be liable for any loss or damage caused by your reliance on any content.